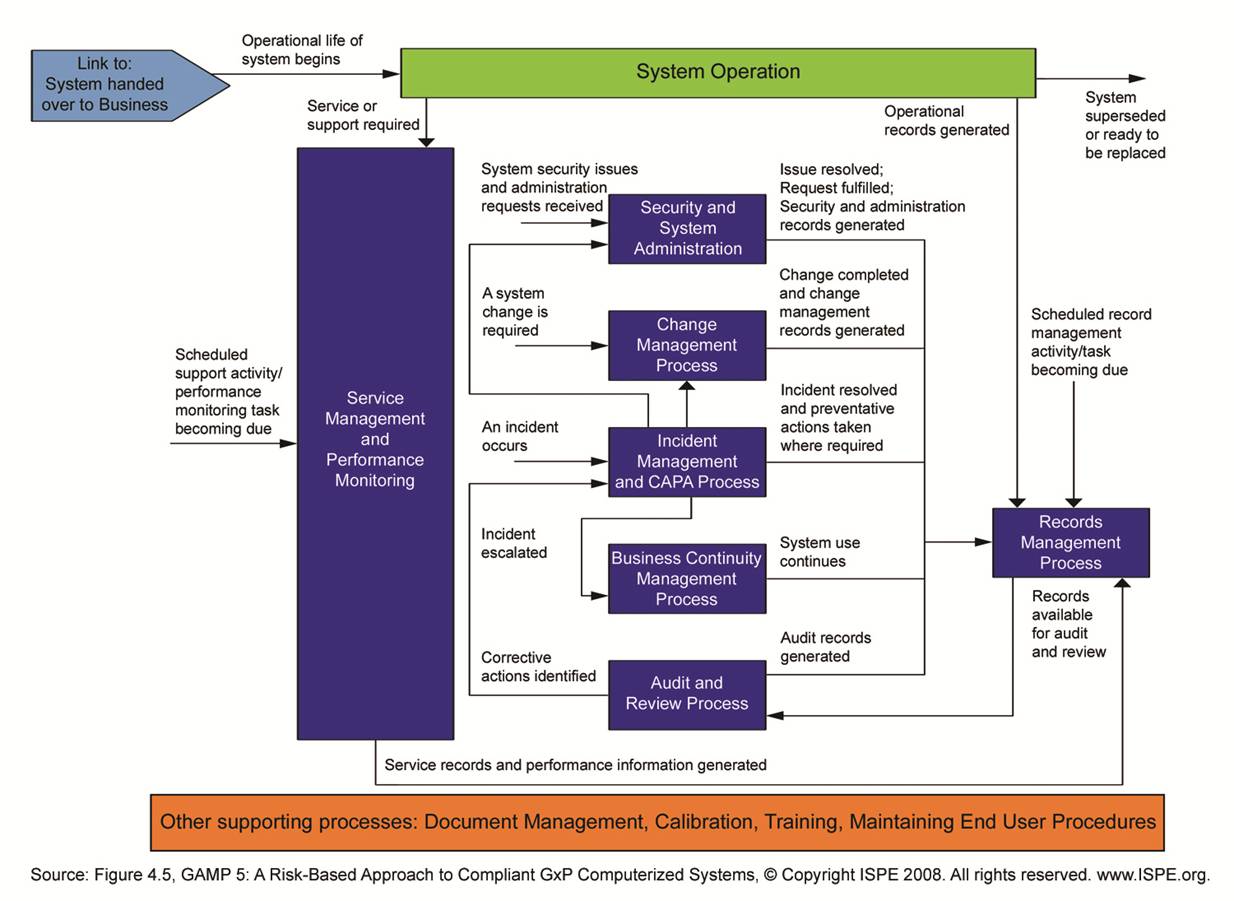
After a successful Project Phase a Validated system is available. The Operation Phase of Validation will ensure that the validated state of the system is maintained during the life cycle of the system. ISPE published a separate Good Practice Guide on this subject.
Major activities and information flows are shown in the diagram below. The diagram divides the processes into the groups Handover, Service Management and Performance Monitoring, Incident Management and CAPA, Change Management, Audits and Review, Continuity Management, Security and System Administration and Records Management.